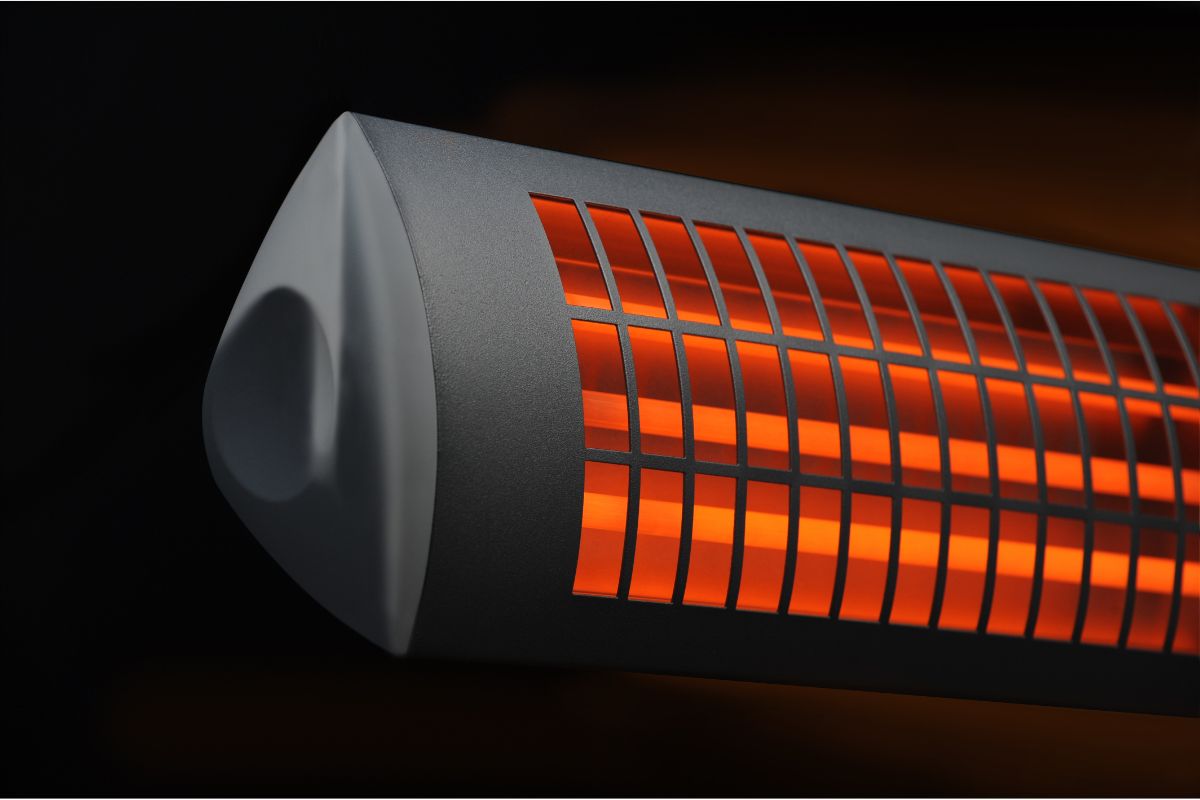
Infrared heating is the process of using radiative heat transfer to heat up an object. The electromagnetic spectrum includes infrared, which has a frequency lower than visible light.
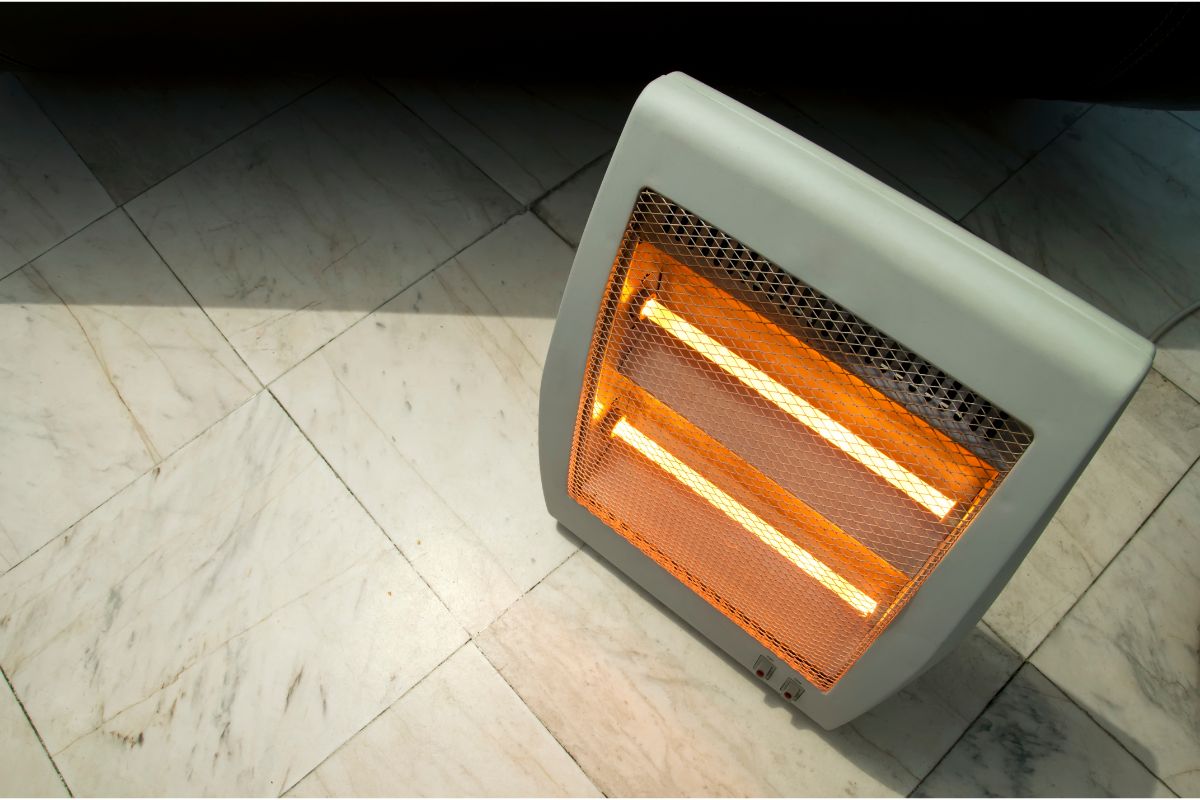

The energy and radiation from the infrared light spectrum are produced by an electrical heating element and then delivered to the target item. In the 1800s, William Herschel identified infrared heat and coined the term “infrared.”
The heaters were formerly encased in ceramic, but this had the disadvantage of absorbing the energy intended for the object of interest.
Quartz heating, often known as short wavelength infrared heating, is a form of radiant heating. Infrared waves are used to actively heat surfaces because all objects emit and absorb infrared heat.
The more heat an object emits, the more warmth it emits. Most quartz heaters use this technology as their foundation.
Quartz is a kind of igneous rock made up of silicon and oxygen molecules, which together produce a rock which is much sturdier than ceramic.
Quartz offers a third useful feature in combination with insulating material and heat resistance. Infrared energy passes through it almost undetectably.
This indicates that the heat generated by the heating source can flow through into the Quartz without becoming absorbed. In this article, we will discuss Quartz heating systems and answer any burning questions you may have about it.
How Do Quartz Heaters Work?
Infrared heaters, such as quartz heaters, are a form of infrared heater. The heating element, which is contained in a quartz tube, produces and disperses heat from the heater.
To produce heat at the specified intensity, the heating component generates heat at the required wavelengths. Infrared seems to be a wave-like radiation that radiates outward from a source of heat and diffuses over time.
From the heat source, electric infrared energy moves in straight lines. Optical reflector devices dilute this radiation into specific patterns.
The heating component in quartz heaters produces heat at specific wavelengths and will provide the precise quantity of heat required.
The quartz tube protects the heating compartment by preventing heat from escaping by convection (Heat loss).
This is in contrast to halogen heaters, which heat a room by emitting radiation from halogen tubes.
As the heating component heats up after an effective powering up, it gets extremely hot. The quartz tube achieves the proper temperature and heat is discharged.
The intensity of heat generated by the quartz heating technique has been examined and determined to be optimal for human health.
The infrared energy is immediately absorbed by persons and items around the quartz heater, with just a little amount of heat being absorbed by the air. This is because the infrared spectrum is almost entirely outside the absorption range of air.
The Different Kinds Of Quartz Heaters
Quartz heaters come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they can differ for a variety of reasons. The following are among the most common quartz heaters:
Wavelength Tube Heaters In The Mid-Range
A heating element is restricted inside a quartz cylinder in the usual layout of a mid-range tubular heater. This may be set up and put in vast spaces to generate massive heating arrays that can be used for a variety of heating purposes.
Tube Heaters With A Short Wavelength
These heaters have a component inside a quartz tube. The main difference is that the tungsten elements are closed and packed with a noble gas, whereas the quartz tubing is not. These heaters are ideal for metals and powdered painting applications.
Heaters With Quartz Panels
A heating element is designed beneath the surface of the quartz panel heater, which has a welded quartz face. Compared to tube heaters, these higher weight heating systems generate an even output across a larger surface area.
Heaters With Furnace Tubes
Winding a heat source around a quartz tube creates furnace tube heaters. The user can appreciate the advantages of both convective and IR heating by placing the heat source exterior rather than the interior of the quartz tube.
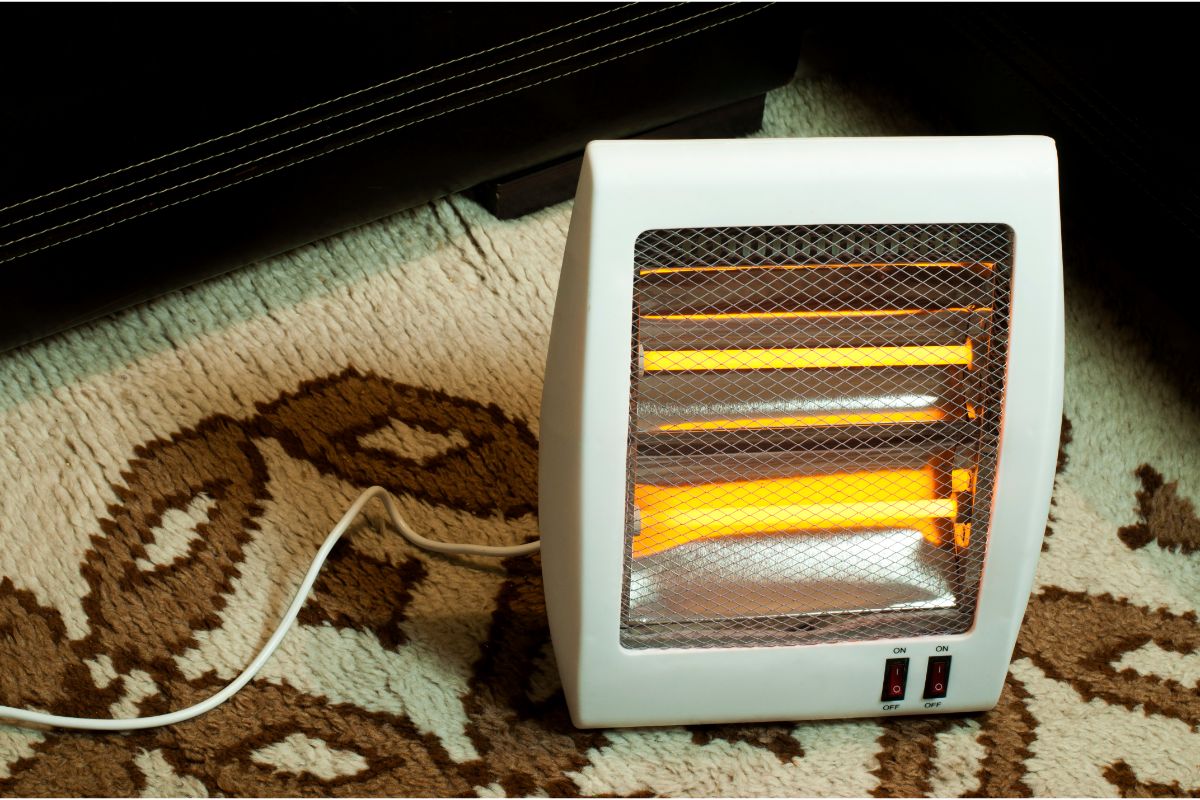

These heaters work best in furnaces where both the atmosphere as well as the surface must be heated to a specific temperature. The function of quartz in all types of quartz heaters is to transfer as much power as possible out from the heat source to the product.
Processes can be finished in very little time with reduced energy consumption if the material utilised in your heater layout does not absorb the energy output. This helps save time and money.
How Energy-Efficient Are Quartz Heaters?
The range of quartz heaters is lost after fifteen feet since they convert one 100 per cent of the electric power input into heat.
Because quartz heaters use a wrapped resistance coil that travels throughout a set of connected tubes, they are extremely efficient.
All of the components are enclosed in a reflective aluminium steel case, preventing loss of heat to the device’s rear. Quartz heaters are designed for instances where you simply have to heat one area while sitting in one place.
For overhead heaters, quartz heating systems are a superior option. Because quartz heaters lack the mass of ceramic heaters, they can reach full working temperature faster.
Using an exterior fan to distribute heat around the room is one technique to enhance energy efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Quartz heating systems produce consistent heat that is rarely interrupted. Quartz heaters are ideal if you need to maintain a consistent temperature for several hours.
Quartz is tough and resistant to heat, but it also doesn’t respond to (or absorb) infrared energy. This means that no infrared energy will be absorbed, and much more warmth will reach where you need it to go.
As a result, you’ll save a lot of money on energy and power expenditures. And, in terms of functionality, it’s essentially identical to a halogen heater.
Sturdy and durable: Quartz warmers are far more robust than ceramic infrared heaters. You won’t be worried over your quartz infrared heating breaking or cracking because it never splits or breaks under extreme temperatures or pressure.
Cheaper in comparison: Ceramic infrared heaters and other types of heaters may be less expensive initially, but they will require a lot of maintenance over time.
However, if you purchase Quartz warmers, you will not have to pay for maintenance and they will operate flawlessly for many years. Similarly, the price of a Quarts heater is far less than the average price of a halogen warmer.
- Discover the Ease and Elegance of Zero-Clearance Fireplaces - July 24, 2023
- How to Build a Frame for an Electric Fireplace Insert: A Step-by-Step Guide - July 16, 2023
- Bedroom Fireplace Ideas That Will Make You Want to Snuggle Up - July 16, 2023